Introduction of Array in C
Array in C Language is a commonly used data structure in C programming. It provides a straightforward and efficient method for storing numerous values under a single name. This article will explore various components of arrays in C language, including their declaration, definition, initialization, types, syntax, advantages, disadvantages, and more.
What is an Array in C?
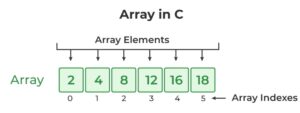
In C programming, an array is a group of data items of the same type that are stored in a specific order in memory. Arrays are used to hold a collection of basic data types like integers, characters, and floating point numbers, as well as more complex data types like pointers and structures.
Arrays are a handy way to keep track of several values in just a single variable, rather than having to create individual variables for every value.
When you want to make an array in a program, you first need to decide the type of data it will hold (for example, integers) and then give it a name using square brackets [].
To insert values into it, use a comma-separated list, inside curly braces:
int myNumbers[] = {2, 4, 8, 12, 16, 18};
We have now created a variable that holds an array of four integers.
C Array Declaration
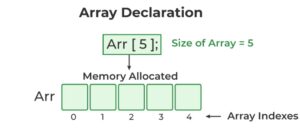
In the C programming language, you need to declare an array just like you would any other variable before you can use it. To declare an array, you need to specify the array’s name, the type of data it will hold, and the dimensions of the array. When you declare an array in C, the compiler sets aside a memory block of the specified size for the array’s name.
Syntax of Array Declaration
data_type array_name [size];
or
data_type array_name [size1] [size2]...[sizeN];where N is the number of dimensions.
Access the Elements of an Array in C
When you want to retrieve a specific item from an array, you need to use its index number.
Array indexing begins at 0, so the first element is referred to as [0]. The second element is [1], and so on.
In this particular case, the code accesses and retrieves the value of the initial element, which is designated by [0], from the array named myNumbers :
Example:-
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int myNumbers[] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
printf(“%d”, myNumbers[0]);
return 0;
}
Output:
25
Introduction to C Basic
- Intro of C
- Arrays
- Strings
- Pointers
- Functions
- Keywords
- Data types
- Structure
- Variables
- Constants
- Identifiers
- Tokens
- Operators
- memory management in the program
- Data structure and algorithm (using C)
Flow Control Statements
- Jump statements
- Goto
- Break
- Continue
- Conditional Statements
- If statement
- If else statement
- Nested if else
- If else if the ladder
- Switch case statement
- Iteration statements
- For loop
- While loop
- Do while loop
- Nested loops
- patterns